What is the Difference Between a Blockchain and a Database?
A database running on the World Wide Web is most often using a client-server network architecture.
A user (client) with permissions associated with their account can change entries that are stored on a centralized server. By changing the ‘master copy’, whenever a user accesses a database using their computer, they will get the updated version of the database entry. Control of the database remains with administrators, allowing for access and permissions to be maintained be a central authority.
This is not at all the same as with a blockchain.
For a blockchain database, each participant maintains, calculates and updates new entries into the database. All nodes work together to ensure they are all coming to the same conclusions, providing in-built security for the network.
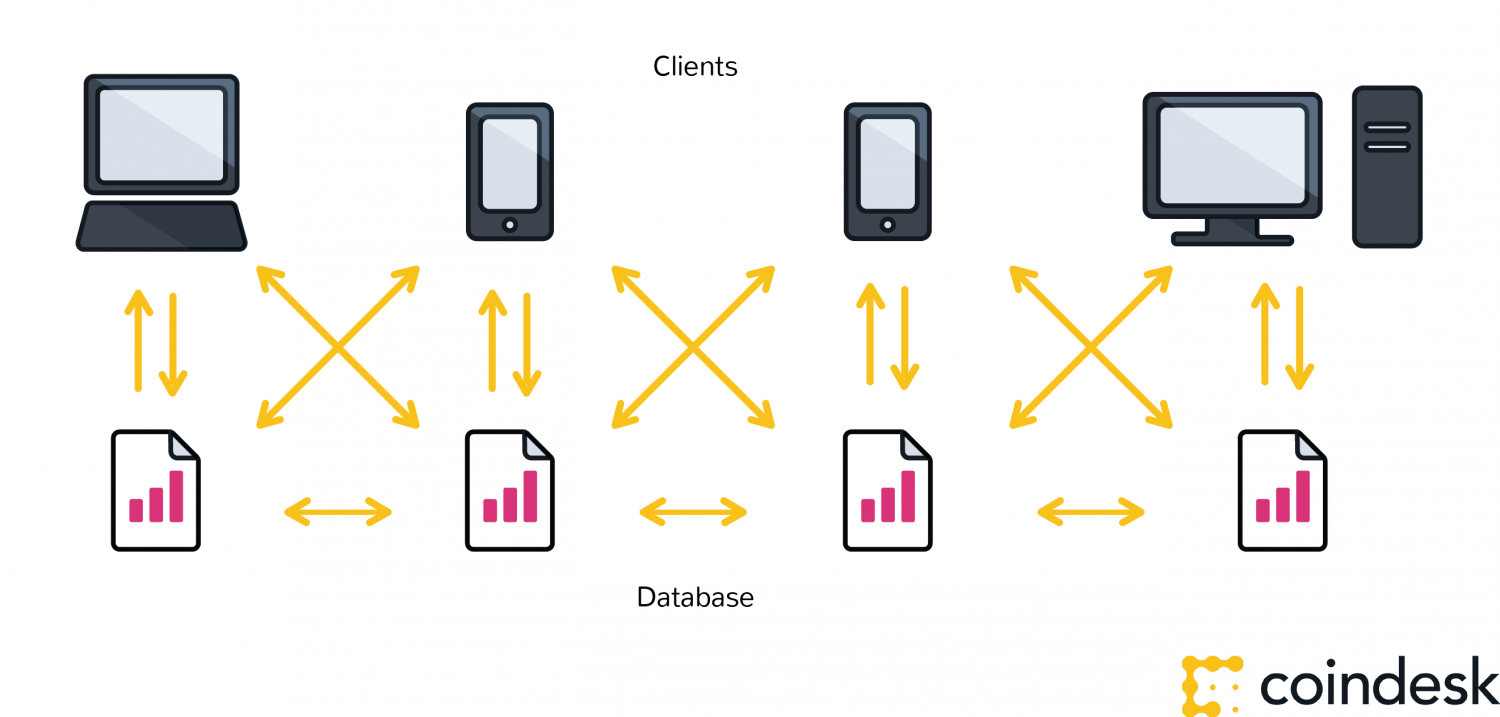
Decentralized control
Blockchains allow different parties that do not trust each other to share information without requiring a central administrator. Transactions are processed by a network of users acting as a consensus mechanism so that everyone is creating the same shared system of record simultaneously.
The value of decentralized control is that it eliminates the risks of centralized control. With a centralized database, anybody with sufficient access to that system can destroy or corrupt the data within. This makes users dependent on the administrators.
Some administrators have earned the trust put in them, for the most part. People’s money is not stolen by banks that record the money they hold in private databases, for example. And, there is a logical reason why you would want centralized control. Centralized control can be a speciality, a reason for being.
But, that also means those with control, such as a bank, need to spend billions of dollars keeping these centrally held databases from being altered by hackers or anyone else who might wish to profit from another’s loss. If the central administrators we’re trusting to keep our information secret fail in this regard, then we lose.
History of itself
Most centralized databases keep information that is up-to-date at a particular moment. They more or less are a snapshot of a moment in time.
Blockchain databases are able to keep information that is relevant now, but also all the information that has come before. Blockchain technology can create databases that have histories of themselves. They grow like ever-expanding archives of their own history while also providing a real-time portrait.
It is the expense required to compromise or change these databases that has led people to call a blockchain database immutable. It is also where we can start to see of the evolution of the database into a system of record.
To read more click here.